Introduction: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) are two therapies gaining significant attention in the field of regenerative medicine. Both PRP and PRF utilise the body's own healing mechanisms to promote tissue repair and regeneration. However, they differ in their composition, preparation methods, and clinical applications. In this article, we'll delve into the nuances of PRP and PRF to understand their differences and the advantages they offer.
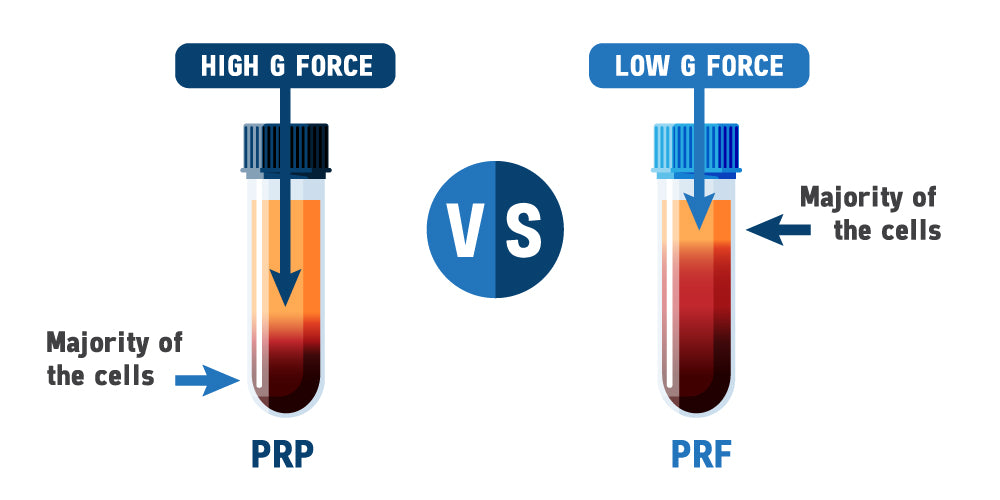
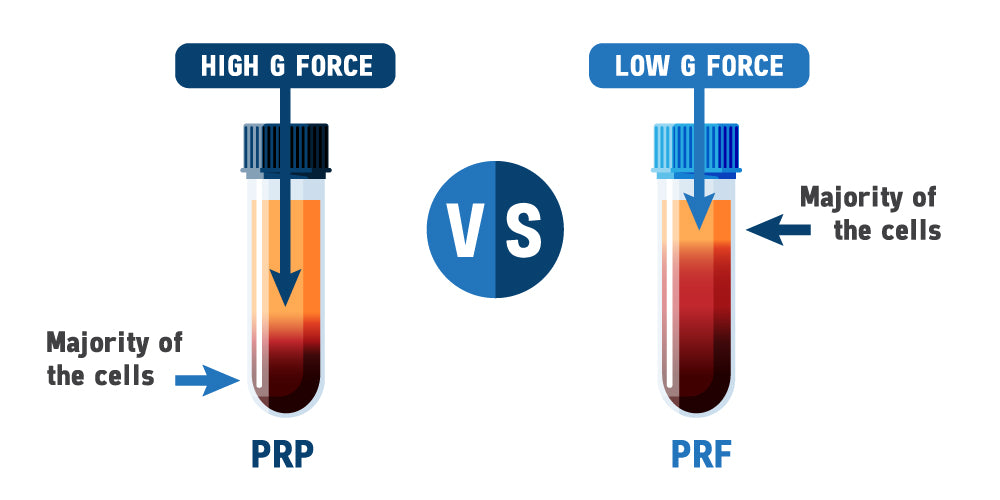
Understanding PRP: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves the extraction of a patient's blood, followed by the concentration of platelets through centrifugation. Platelets contain growth factors and other bioactive proteins that play a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration. Once concentrated, the PRP is injected into the target area, stimulating the body's natural healing response.
Exploring PRF: Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) is a more advanced form of platelet therapy that involves the preparation of a fibrin matrix along with platelets and leukocytes. Unlike PRP, PRF is processed without anticoagulants, allowing for the formation of a dense fibrin network that traps growth factors and facilitates a sustained release over time. This matrix provides a scaffold for cell migration and proliferation, enhancing the regenerative process.
Key Differences:
- Composition: PRP primarily consists of platelets suspended in plasma, while PRF contains platelets, leukocytes, and fibrin matrix.
- Preparation: PRP requires centrifugation to separate platelets from other blood components, whereas PRF preparation involves a slower centrifugation process without anticoagulants.
- Release of Growth Factors: PRF offers a sustained release of growth factors due to the fibrin matrix, promoting prolonged tissue regeneration compared to PRP.
- Clinical Applications: While both therapies are used for tissue repair and regeneration, PRF may be more suitable for applications requiring a longer-lasting effect, such as bone regeneration and wound healing.
Conclusion: In the realm of regenerative medicine, PRP and PRF stand out as effective therapies for promoting tissue repair and regeneration. While PRP offers a concentrated dose of platelets, PRF provides a more complex matrix that sustains the release of growth factors over time. Understanding the differences between PRP and PRF is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike to choose the most appropriate treatment for their specific needs. Whether it's accelerating wound healing, enhancing skin rejuvenation, or promoting musculoskeletal repair, PRP and PRF continue to revolutionise regenerative medicine and offer hope for patients seeking natural and effective solutions.